In the September 11, 2018 Ask The Headhunter Newsletter an employee placed by an employment agency quit, and the employer wants the placement fee refunded.
Question
An employee quit without notice after five months. Her explanation was that she never wanted to stay at this job from the start. We paid a hefty agency fee for this person. She never signed any paperwork with the agency, and the contract stated that employment is “at will.”
Do we have the right to go after the employee to pay us back for not being truthful? Or do we have to go to the hiring agency to see if we can get our money back?
Nick’s Reply
An awful lot of readers are laughing at your story right now, rolling their eyes, and thinking, “Serves you right!”
Why would anyone laugh? Because the recruiting and hiring process usually blows up in the job seeker’s face — not the employer’s.
But I’m not here to laugh at you. The rise of intermediaries in the hiring process has introduced mass confusion, frustration and finger-pointing on every side — employers, agencies, employees. I’m afraid everyone is culpable.
You paid the employment agency, not the employee
I can’t believe you’re serious about recovering the fee you paid to the agency from the employee. I doubt you have a contract with the employee that provides such recourse. If there’s a contract at all, it’s between your company and the agency. Take it up with them.
If the agency does a good job for you in general, don’t blame them. Once you’ve got the hire for five months, whatever happens next is a management problem, not a placement problem. You chose to make — and keep — the hire.
But first consider the pickle you’ve put yourself in.
The problem with middle men
Employers expect someone else is going to handle recruiting and hiring for them, then are shocked when things go awry. Most agencies play fast and loose because they get paid to fill a job, not to deliver the best hire, and everyone suffers for it. Job seekers suspend their common sense when someone they don’t know dangles an “opportunity” in front of them. The introduction of middle men in hiring creates chaos, poor management and terrible decision making.
In this case, everything depends on the contract you have with the employment agency, and on whether there is a guarantee on the placement that provides for a refund.
The number of employment agencies — which go by all kinds of monikers — has exploded, with the result that employers often have no idea who they’re dealing with. (See They’re not headhunters.) It’s an unusual occurrence, but it’s possible the recruiter and your new hire were in cahoots and planned the “placement” to last only until the fee guarantee expired. Then they split the fee you paid and moved on to the next sucker company. I always explore this possibility when a new hire lasts just past the guarantee, which is usually between 30 and 90 days.
But I repeat: If your agency does good work in general, then they may not be the problem at all.
There are some measures you can take to avoid the most obvious problems with agencies.
Get a guarantee from employment agency
Always have a written contract with the recruiter that includes a pro-rated guarantee period. That is, if the new hire “falls off” for any reason — whether you fire them or they quit — make sure you can get back some or all of the fee you paid. Such guarantees usually run 30-90 days and will offer a refund or replace the employee. Good agencies will negotiate reasonable terms with you.
If the contract suggests the hire will be responsible for any refund to you, run. That’s unethical and unscrupulous, and possibly illegal.
Get a no-poach agreement
Your contract with the agency should prohibit poaching. That is, the agency cannot recruit the person it just placed with you — or any other employee at your firm — for a year or more after the last placement the agency made at your firm. This can be even more restrictive if it prohibits placing anyone who has left your firm in the past year or more. Some headhunters don’t like such clauses, but they promote healthy business relationships.
I would nose around. Did the agency that placed the employee with you recruit her out or place her elsewhere? Good agencies never do that.
Understand that “at will” employment cuts both ways
As I said above, it’s usually employees who complain about being terminated without any explanation in states where employment is “at will” by law. What’s your company doing to make sure it’s a good place to work?
Barring some kind of contractual obligation or regulation, you can no more prohibit someone from quitting a job than you can be prohibited from terminating them.
Check the agency’s references
Check the employment agency’s references as well as the specific recruiter’s references before you do business with them. I’ll estimate that 90% of pitches you get from recruiters will end when you ask them for references. Work only with recruiters whose skills and reputations you have confirmed, or don’t be surprised at the consequences.
What to do next
At the very least, I’d call the agency in for a face-to-face meeting to discuss what happened as well as the terms for next assignment. Assess whether you trust the recruiter. I would not necessarily blame the recruiter if they did everything else right.
If your relationship with the agency is at e-mail’s length because they’re not in your city, then consider the value of working only with local agencies.
But don’t expect any agency is going to refund your money after five months. Read the refund deal in your contract. Some of this falls on you, but I understand your frustration. New employees feel the same way when they quit a job for a new one — only to get fired suddenly a few months later without explanation.
If you learned too late that the employee didn’t really want the job from the start, I suggest you improve your recruiting and interviewing processes — and how you manage. Always remember that while you can fire at will, an employee can quit at will. (This depends on the laws in your state.) I’m not a lawyer but my guess is, if she did the work and you paid her for it, no one is obligated to continue the employment — you or her. It’s up to you to get to know your workers well.
You should check with a lawyer so you’ll know better next time, but chalk this one up to experience.
This is one reason why it’s worth cultivating your own pipeline for recruiting through your own trusted sources who will put their own reputations on the line when they recommend someone. If you’re going to use an agency, it’s best to meet a good one through your trusted sources before a lousy agency takes advantage of you.
If you’re an employer, what’s in the contracts you sign with employment agencies? How do you protect your company? If you’re a headhunter, recruiter or employment agency, how do you help ensure your client’s (the employer’s) satisfaction? If you’re the hire who was placed by the agency, would you consider refunding part or all of the recruiter’s fee if you decided to quit the job?
: :

 When I was given my performance review they told me I was at the top end of my salary grade. Instead of a raise, I was given a 3% bonus that came on my last paycheck. Depending on the outcome of a recent job interview at another company, I might be resigning in a few days.
When I was given my performance review they told me I was at the top end of my salary grade. Instead of a raise, I was given a 3% bonus that came on my last paycheck. Depending on the outcome of a recent job interview at another company, I might be resigning in a few days.
 6. “Because their technology is smart.”
6. “Because their technology is smart.” Zip offers no success-rate metrics (audited or otherwise) about hiring or getting hired. The guy in the commercial does that.
Zip offers no success-rate metrics (audited or otherwise) about hiring or getting hired. The guy in the commercial does that. I’ve been around the block a few times, that is, I’ve changed jobs. It was never easy, except for one job I got from a personal referral without even a job interview. But nothing prepared me for changing professions. I’ve all but concluded it’s impossible. Even if I could do it, now I question whether it’s worth it because of the haircut I’d have to take in pay.
I’ve been around the block a few times, that is, I’ve changed jobs. It was never easy, except for one job I got from a personal referral without even a job interview. But nothing prepared me for changing professions. I’ve all but concluded it’s impossible. Even if I could do it, now I question whether it’s worth it because of the haircut I’d have to take in pay.
 Nick’s Reply
Nick’s Reply I could write this column forever and not run out of material because you give me tons of great questions about job hunting and hiring, and each week I give you advice. But I have no delusion that it’s the best advice because the best advice surfaces in the discussions we have every week about whatever topic we’re covering.
I could write this column forever and not run out of material because you give me tons of great questions about job hunting and hiring, and each week I give you advice. But I have no delusion that it’s the best advice because the best advice surfaces in the discussions we have every week about whatever topic we’re covering. Next month I’ll have my three-year performance evaluation, and I feel that I am worth more than my current salary. How do I convey the message that my job is worth more and ask for more money?
Next month I’ll have my three-year performance evaluation, and I feel that I am worth more than my current salary. How do I convey the message that my job is worth more and ask for more money? We had a candidate go through the interview process and the offer cycle at our company. He took a position for a week, then returned to his other job. He never gave notice to his other employer, just took vacation time. After working the week, he didn’t return. It took a couple of days to track him down at his old work number. Is this common?
We had a candidate go through the interview process and the offer cycle at our company. He took a position for a week, then returned to his other job. He never gave notice to his other employer, just took vacation time. After working the week, he didn’t return. It took a couple of days to track him down at his old work number. Is this common? Every month the Department of Labor issues the “jobs numbers” and the “unemployment numbers” and everyone goes gaga about how great things are. There are loads of jobs to apply for! There’s a shortage of talent, so that’s good tidings for us job seekers! You’d think simple market economics would mean higher salaries and job offers.
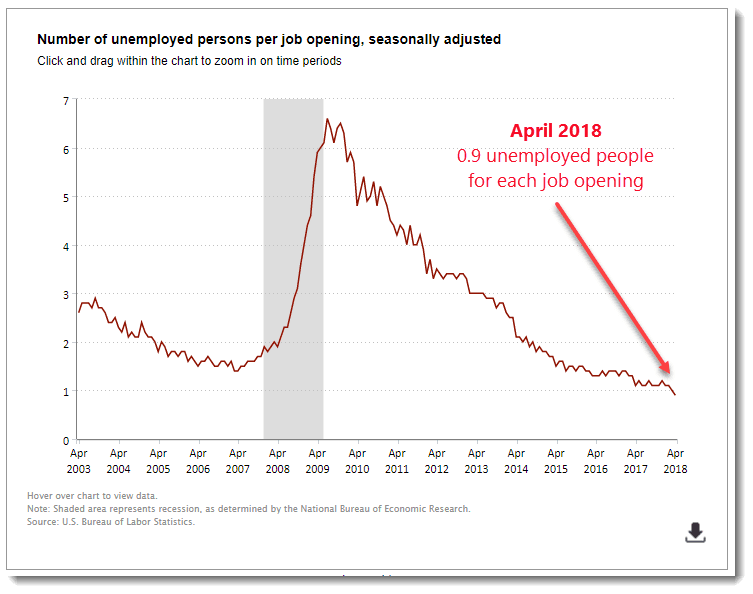
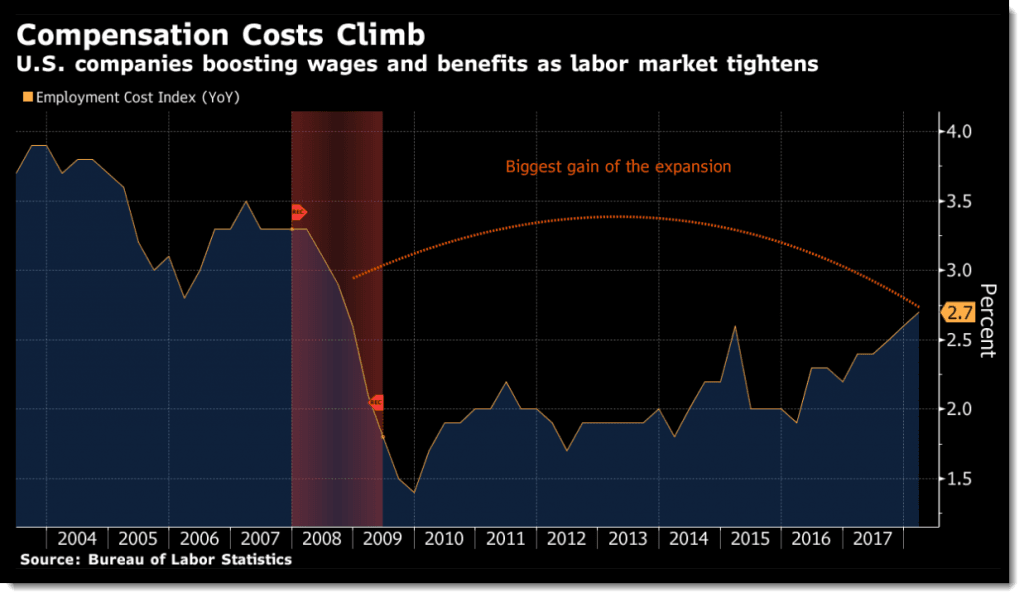
Every month the Department of Labor issues the “jobs numbers” and the “unemployment numbers” and everyone goes gaga about how great things are. There are loads of jobs to apply for! There’s a shortage of talent, so that’s good tidings for us job seekers! You’d think simple market economics would mean higher salaries and job offers.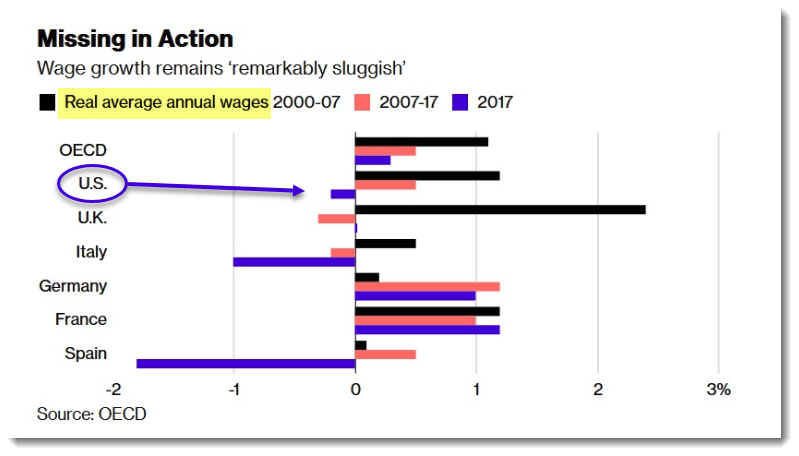
 I was given an official job offer. The letter stated that if I met the conditions of the job offer (and it listed the conditions) that the offer would be finalized.
I was given an official job offer. The letter stated that if I met the conditions of the job offer (and it listed the conditions) that the offer would be finalized.