In the July 10, 2018 Ask The Headhunter Newsletter a reader asks whether the news about jobs creation isn’t a load of crap.
Question
 Every month the Department of Labor issues the “jobs numbers” and the “unemployment numbers” and everyone goes gaga about how great things are. There are loads of jobs to apply for! There’s a shortage of talent, so that’s good tidings for us job seekers! You’d think simple market economics would mean higher salaries and job offers.
Every month the Department of Labor issues the “jobs numbers” and the “unemployment numbers” and everyone goes gaga about how great things are. There are loads of jobs to apply for! There’s a shortage of talent, so that’s good tidings for us job seekers! You’d think simple market economics would mean higher salaries and job offers.
But it’s not true. I don’t see higher pay or even higher job offers, not at any meaningful level. Employers aren’t hiring any faster or acting more competitive. Taking two months to decide to make a job offer isn’t the sign of a tight labor market. And demanding my salary history so they can low-ball me on a job offer doesn’t look like companies are struggling to fill jobs.
What’s your take? Am I missing something or is the jobs euphoria in the news just B.S. cranked out by stoned experts?
Nick’s Reply
The jobs euphoria is B.S.
Since last year I’ve been collecting samples of the reports you’re talking about, and there’s a dirty little secret that the pundits and politicians keep trying to bury in the news — but like a nasty case of the hiccups, it’s impossible to hide.
Politicians, the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) and the media have been reporting on exciting gains in job creation. The U.S. created 213,000 new jobs in June (MarketWatch, July 6, 2018) and monthly jobs growth has been positive for the past several years. That seems to be a good sign, but for what and to whom?
According to the DOL’s Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) JOLTS report (Job Openings and Labor Turnover) issued June 5, there were 6.7 million jobs open in the U.S. at the end of April. On July 6 the BLS reported that 6.6 million people were unemployed. That means there are more jobs that need to be filled than there are unemployed people.
It’s a 5-alarm fire!
With every new report, economists say they’re flummoxed. With labor in such short supply, the surfeit of demand to fill vacant jobs suggests employers would bid up salaries and wages to get the workers they need — especially if they expect to lure people with jobs away from other employers.
By no stretch of the data is that happening. In a bluntly cynical July 5 Forbes article, Byron Auguste reports that “Three decades of stagnating wages—rising just 0.2% annually since the early 1970s, adjusted for inflation—means an economic five-alarm fire.”
While economists, analysts and politicians struggle to explain wage stagnation by blaming a “skills shortage” (improperly skilled workers are not worth higher wages) and a failure of workers to “re-educate” themselves, Auguste refers to the “skills gap narratives” as “the usual suspects” in the never-ending rationalizations about why companies aren’t paying salaries commensurate with market demand.
“The U.S. has arrived at an inflection point in our economy, technology and demography that demands a reality check on the sorry state of our labor market, and the – i.e., our – institutional practices that produce it,” writes Auguste.
Remember that phrase: institutional practices. We’ll come back to it. But first, I want to throw some spaghetti against the wall, and I hope you can help me read something useful in the patterns it makes.
Where’s the money?
Virtually every new report about “more jobs” includes an embarrassing parenthetical gotcha. It goes like this:
This hand-wringing about the wage numbers in the face of unprecedented jobs growth isn’t new. On December 8, 2017 USA Today reported:
The labor market remained healthy in November, adding jobs at a strong clip despite a shrinking pool of available workers. Still, there were some potentially troubling trends for employees, most notably persistently sluggish wage gains.
“Some potentially troubling trends?” Oops! For months, little side notes like this have appeared in report after report (I think this is what the news media mean by “full disclosure”), then these afterthoughts get buried under the euphoria of politically stoned economists and pundits, and beneath the proclamations of “good times are here!”
“The June ’18 employment report showed a drop-off from May in both the rate of hiring as well as the wage increase year over year,” said Paychex president and CEO Martin Mucci. “We saw for the first time that the annual wage increase dropped below 2.5 percent, which is pretty surprising given the tight labor market. That seems to be the big question out there. Small businesses have a little bit of a harder time hiring workers in a tight labor market so you’d expect that to be going up.”
–Accounting Today, July 3, 2018:
Paychex sees wage and job growth slowdown at small businesses in June
Lousy wage increases are “pretty surprising,” eh? “So you’d expect [wages] to be going up,” eh? No kidding.
Typically, wages pick up at this point of an economic cycle because a low jobless rate forces companies to boost wages to find workers… Wage growth in Ohio and the U.S., tepid for the most part since the end of the Great Recession, is starting to show signs of getting weaker… It’s a trend that has baffled economists and others. “Everybody is really perplexed about why that is,” [said Frank Fiorille] vice president of compliance, risk and data analytics for Paychex].
–The Columbus Dispatch, July 3, 2018:
Bad sign for workers — wage growth getting weaker for many
Everybody is really perplexed!
ZipRecruiter says everything is cool!
Here’s my favorite. CNBC calls it exactly what it is in the title of this July 6, 2018 article: The jobs “conundrum” continues: “How are we not getting higher wages?” But then CNBC lets an economist from ZipRecruiter (economist or marketer?) spin it to keep perplexed job seekers searching for temp jobs that pay less than, well, an economist-cum-marketing-manager makes at ZipRecruiter:
“While the wage growth rate didn’t increase this month, having it hold steady is a good sign,” said Cathy Barrera, chief economist at ZipRecruiter, an online employment marketplace.
Lousy wage growth is a good sign! ZipRecruiter couldn’t care less what wages are, as long as jobs remain unfilled and employers keep posting them, and job seekers keep clicking them. That’s how Zip and other job boards make money. It’s all good, folks!
Does it matter that there are more new jobs every month? Probably. Unless you’re a middle manager who just lost her job making $95,000 with good benefits, and now you’re looking down the barrel of a fly-by-night recruiter’s job posting for a contracting job that pays $23 an hour — and the guy ghosted you after you filled out 9 pages of online forms and sat for a nerve-racking video interview with an algorithm.
It’s a good sign there are loads of jobs out there for you to apply for on ZipRecruiter, dontcha think?
CEO jobs pay well!
Let’s put all this euphoria into some context. People are starting to ask questions about all that job growth.
Must be the skills shortage — it seems not enough blue-collar workers are getting the re-education they need to apply for a job that pays better in today’s new world. Like CEO.
CEOs of America’s 350 largest firms made an average of $15.6 million in 2016…or 271 times more than a typical worker in 2016…While the CEO-to-worker compensation ratio of 271-to-1 is down from 299-to-1 in 2014 and 286-to-1 in 2015, it is still far higher than the 20-to-1 ratio in 1965 or the 59-to-1 ratio in 1989.
–Economic Policy Institute, July 20, 2017:
Top CEOs took home 271 times more than the typical worker in 2016
Oops. Where, indeed, is the money going in this booming economy?
Are consulting jobs sucking wages out of the economy?
Okay, I’ll stop. I’ve got loads more, but you get the point.
The euphoria is generated to keep you down on the farm. While economists and analysts blame pathetic wage increases on workers who are too lazy or too stupid or too complacent to re-educate themselves for today’s modern jobs, I’ve got another explanation. I think this is part of what Byron Auguste is referring to when he cites “the sorry state of our labor market” and points to the “institutional practices that produce it.”
Temporary, part-time, contracting jobs that companies are substituting for full-time, permanent jobs are sucking the wages out of our economy.
We’ve discussed it here before: Consulting: Welcome to the cluster-f*ck economy. Contracting gigs are one of the institutional problems that shift profits to CEOs, investors and employers and keep wages low. Why’s that so hard for economists to understand?
BenefitsPro spills the beans to the folks who manage corporate benefits programs in a July 6, 2018 article: Stagnant wage growth driving worker dissatisfaction:
Another culprit is an increase in temporary or part-time work, an issue that’s come to a head in Italy, with businesses clashing with the new government over plans to restrict temporary contracts.
Is supply-and-demand dead?
BenefitsPro includes a tasty graph whose blue lines put the U.S. on the same side of the world economic story as Italy. (Source: Organization fro Economic Cooperation and Development.)
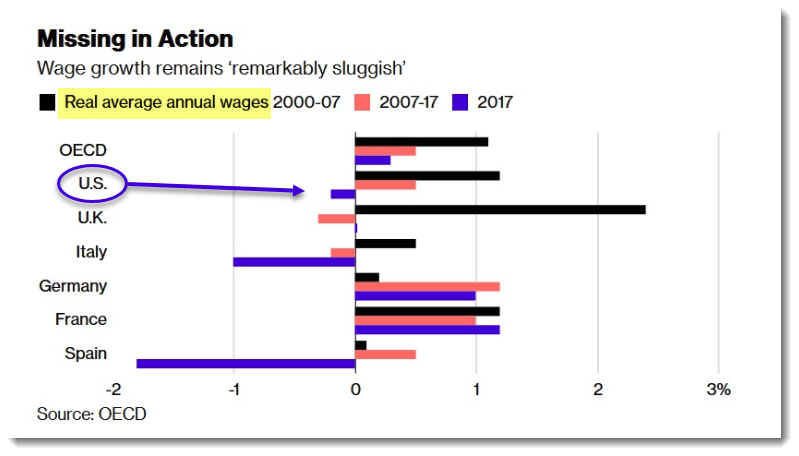
Economists might have an Aha! moment if they study that graph side by side with this graph from the BLS, which is cited in a July 10, 2018 JOLTS news release:
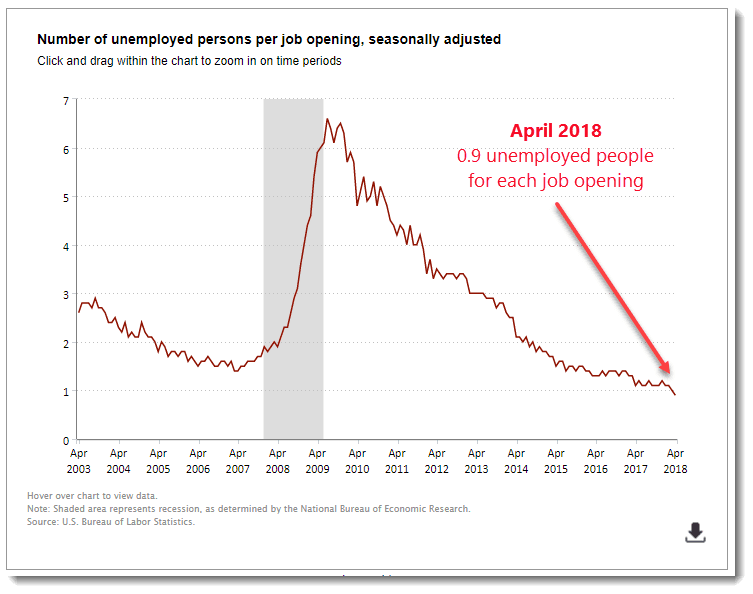
How could “real average annual wages” be lower in 2017 than over the past 10 years when there are more jobs vacant than there are unemployed people? Is the relationship between supply and demand really dead?
Where does the money go?
Let’s go back to one of the precious quotes above, from The Columbus Dispatch:
“Typically, wages pick up at this point of an economic cycle because a low jobless rate forces companies to boost wages to find workers…”
Well… you’d think so, when corporate profits are up and employers are paying their CEOs 271 times more than the typical worker. You’d think so, when Congress passes tax breaks that are supposed to trickle down to everyone that works. So WTF is going on?
Let’s go back to the BLS. I love this little graph, based on BLS statistics and published by Bloomberg last April. It shows the employment cost index — what companies spend on compensation:
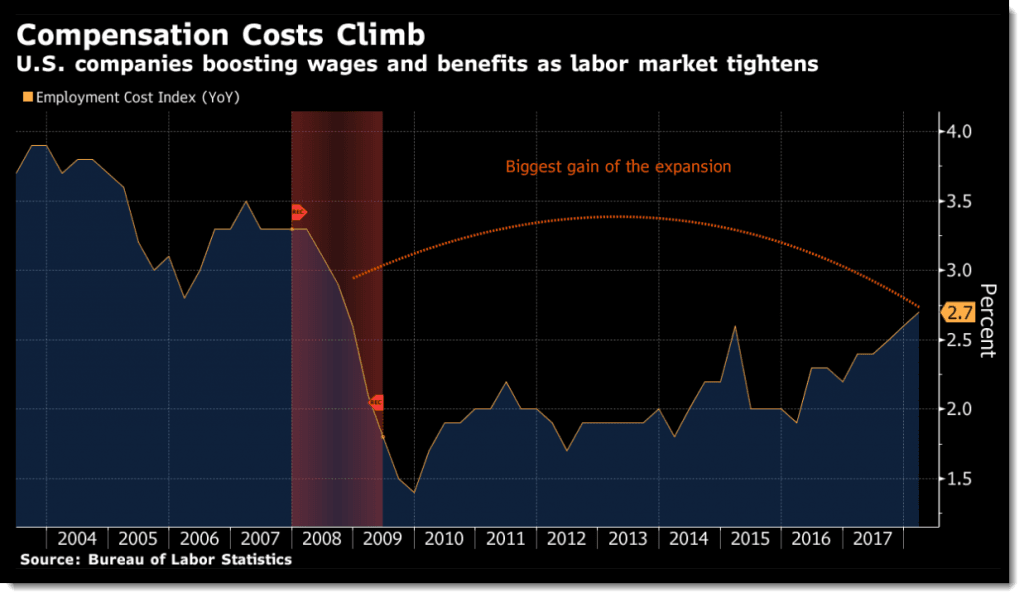
The accompanying text bemoans that “employment costs rose more than expected in the first quarter and a measure of private wages had the biggest annual gain since 2008.” What Bloomberg doesn’t note is that way over on the left side of that graph U.S. companies were sharing a whole lot more with their workers. What companies spend on compensation today is still way down from a 2003 high, and current compensation costs still have not “recovered” to even 2007 levels. (Yah, I can see — there was a recession around 2007-2008 but, hey, do I look like an economist?)
(The share of profits that companies spend on workers varies by industry. See my column on PBS NewsHour: Which industries are being too greedy to pay you fairly?)
When the economy is booming, profits are up, and companies are so awash in cash that they demand the freedom to invest it in elections — why is anyone at a loss to explain why we’re not seeing higher wages?
If you can’t re-tool your skill set to be a CEO, you could try one of those online investment courses, so you could make a living at your PC — as an investor!
What was your question?
When I can’t figure something out, sometimes I give myself room to rant. I cut out articles, data, graphs — and I spread them out on the floor, hoping I can puzzle them up into an answer that makes sense to me. Forgive me if I’ve ranted too long.
But if I threw one or two bits of information up on your screen that give you pause to think about this strange economy and job market in a new way, maybe it’s worth it.
Let’s go back to the question in this Q&A:
“You’d think simple market economics would mean higher salaries and job offers… Am I missing something or is the jobs euphoria in the news just B.S. cranked out by stoned experts?”
Wages and salaries are basically stagnant, and more people are admitting it. Employers are spending less on wages and salaries because they’re renting temporary workers from “consulting firms.” But the bucks are there. They’re just going to somewhere (and to someone) other than the labor pool.
So I think the euphoria about “jobs creation” is indeed B.S. because more new jobs during a labor shortage without higher wages is not good news — it tells us something is very wrong. It’s B.S. because what’s being created is a phantom industry of middle-men that suck value out of our economy. (See The Job Monopoly: How companies keep pay low.)
Where will it end?
How long can the economy — which is people, after all (and there are more workers than CEOs) — withstand this scenario?
I dunno. There’s an old saw about profits: Pigs get fat. Hogs get slaughtered.
Billionaire Nick Hanauer, a staunch advocate for higher minimum wages, says it best: “The pitchforks are coming.”
Do the “jobs creation” numbers and stagnant wage growth make sense to you? Are workers really so incorrectly skilled that it explains why they’re not getting the jobs employers say they’re dying to fill? I blame some of it on our “consulting economy.” If you study the spaghetti on the wall, what do you see? Is the jobs euphoria justified?
: :
 While employers demand to know all your salary information prior to an interview, they don’t disclose the salaries of jobs they post. They want you to apply blindly, hoping to snag you into rationalizing lower pay after you’ve invested hours filling out forms and interviewing. (This is the old “foot-in-the-door” sales method.)
While employers demand to know all your salary information prior to an interview, they don’t disclose the salaries of jobs they post. They want you to apply blindly, hoping to snag you into rationalizing lower pay after you’ve invested hours filling out forms and interviewing. (This is the old “foot-in-the-door” sales method.)




 Most of your readership seems to be in relatively high-salary jobs but I have a question about lower-level jobs. I hope you think it’s worth covering. I see the federal minimum wage is in the news again because the new administration is trying to push through an increase. You published a Q&A column almost exactly a year ago arguing for a national $15 minimum wage
Most of your readership seems to be in relatively high-salary jobs but I have a question about lower-level jobs. I hope you think it’s worth covering. I see the federal minimum wage is in the news again because the new administration is trying to push through an increase. You published a Q&A column almost exactly a year ago arguing for a national $15 minimum wage
 I’ve been unemployed for six weeks. Was earning around $120K. Have been offered a position at $85K and, quite frankly, I need the money. Even more important, I recognize that my self-esteem is too bound up in my career: I need to work for more than just the money. Am seriously considering accepting this lower offer, because I believe these folks cannot afford to pay more. Will my chances of negotiating another position at a higher salary be irrevocably damaged if I accept a salary cut? Advice, please, and thanks in advance.
I’ve been unemployed for six weeks. Was earning around $120K. Have been offered a position at $85K and, quite frankly, I need the money. Even more important, I recognize that my self-esteem is too bound up in my career: I need to work for more than just the money. Am seriously considering accepting this lower offer, because I believe these folks cannot afford to pay more. Will my chances of negotiating another position at a higher salary be irrevocably damaged if I accept a salary cut? Advice, please, and thanks in advance.






 Every month the Department of Labor issues the “jobs numbers” and the “unemployment numbers” and everyone goes gaga about how great things are. There are loads of jobs to apply for! There’s a shortage of talent, so that’s good tidings for us job seekers! You’d think simple market economics would mean higher salaries and job offers.
Every month the Department of Labor issues the “jobs numbers” and the “unemployment numbers” and everyone goes gaga about how great things are. There are loads of jobs to apply for! There’s a shortage of talent, so that’s good tidings for us job seekers! You’d think simple market economics would mean higher salaries and job offers.


 During my Christmas break, the news kept coming hot and heavy from the U.S. Department of Labor and associated pundits and experts: You should stop complaining about jobs and salaries. Everything’s great!
During my Christmas break, the news kept coming hot and heavy from the U.S. Department of Labor and associated pundits and experts: You should stop complaining about jobs and salaries. Everything’s great!